Dystonia is often mistaken for spasticity, yet the two conditions behave and need to be managed very differently. Spasticity involves increased muscle tone and resistance to movement, whereas dystonia is a movement disorder where muscles contract involuntarily, creating twisting, repetitive, or fluctuating movements. These movements can be slow or rapid, and may affect a single region (such as the neck or hand) or the entire body.
Jump straight to…
What Is Dystonia?
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder in which the brain sends abnormal signals that cause muscles to contract involuntarily. These contractions can be sustained or intermittent, leading to twisting, repetitive movements or abnormal postures.
Dystonia can affect a specific part of the body (known as focal dystonia), several adjacent areas (segmental dystonia), or be widespread and affect many areas (generalised dystonia).
What causes dystonia
The condition can appear in childhood or adulthood, and sometimes arises after injury, brain conditions, or as a result of genetic factors, but in many cases the exact cause remains unknown.

Symptoms
Symptoms vary widely depending on which muscles are affected. Common presentations include involuntary twisting of the neck (when neck muscles are involved), uncontrolled spasms of the limbs, or odd posture of the trunk or extremities.
Stress, fatigue, or certain voluntary actions often exacerbate dystonic movements.
Need Specialist Seating?
The Case for Dynamic Seating
Because dystonia is variable, seating strategies must be dynamic to accommodate it. Traditional postural management techniques that work for spasticity generally do not work for dystonia, and can even make symptoms worse.
A growing body of research is supporting what many clinicians have observed for years: children and adults with dystonia do better in seating systems that move with them rather than against them.
In 2020, Gimeno and Adlam hypothesised that “whole-body dynamic seating can improve comfort, activity, participation and quality of life in young children with dystonic cerebral palsy.”
Their work on “Dystonia and Dynamic Seating” highlights a critical shift in thinking: comfort and functional ability are maximized when the seating system absorbs movement instead of resisting it.
When the body is allowed to move, the nervous system experiences less resistance, which can reduce the force, frequency, or discomfort associated with dystonic contractions.
Key Seating Rules for Dystonia
Don’t try to ‘fix’ the posture
Dystonia is not something that can be held still. Attempts to restrain the body often increase involuntary movements, raise muscle tone, and create pain or frustration.
Instead, the aim should be to support the body in a way that provides a “safe space to move” without restricting natural patterns.
Register for our Posture Webinar
Flexible seating
Dynamic components such as flexible backrests, pelvic supports, padded footplates and dynamic head supports help absorb the energy generated by dystonic movements. This improves comfort and alignment and allows for range of movement, without forcing a position the body cannot sustain.
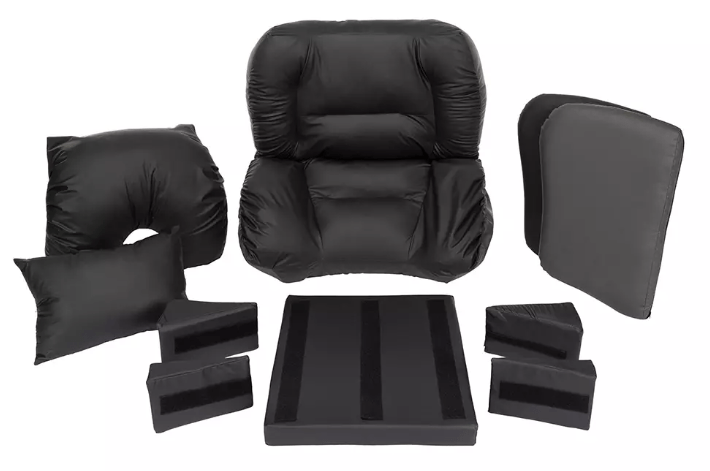

Postural accessories and supports
Build stability from the pelvis
A stable base is still essential for people with dystonia. A well-supported, well-aligned pelvis provides a foundation for the rest of the body to move more efficiently. Use contoured cushions, pelvic belts that guide but don’t restrict, and materials that cushion impact during movement.
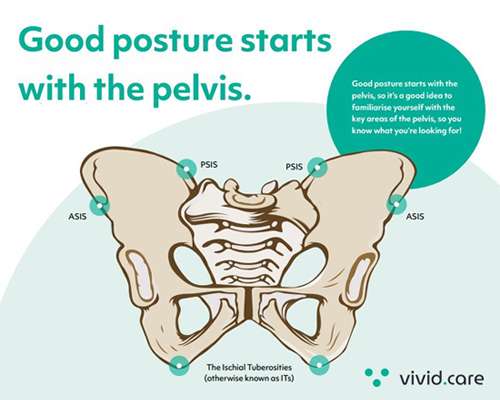
Areas of the Body Often Affected in Seating
Dystonia can influence any part of the body, but in seating systems clinicians often pay special attention to these areas:
Neck
Neck dystonia can cause twisting or turning of the head, rapid, unpredictable changes in position, and sometimes pain.
Rigid headrests can trigger increased force or even injury. Dynamic head supports, flexible positioning, or systems that ‘follow’ the head’s movement tend to work best.

Hands and Forearms
Involuntary movements of the upper extremities can make using trays difficult and may increase frustration or fatigue. Support strategies include:
- Forearm troughs that allow gliding movement
- Soft-surface trays
- Flexible arm supports that accommodate rather than resist motion
Seating Goals for Adults and Children with Dystonia
The ideal seating system should:
- Allow safe movement rather than preventing it
- Reduce force and energy expenditure during dystonic episodes
- Promote comfort over long sitting periods
- Enable participation in play, communication, and mobility
- Adapt as patterns of movement change throughout the day
When seating supports movement, people with dystonia often show improvements in attention, breathing, communication, and overall quality of life.
Try Our Chair Selector Tool
Recommended Chairs for Dystonia
Here are some of the seating features that align with the principles above and may suit individuals with dystonia or dystonic cerebral palsy.
| Seating Feature | Why It’s Suitable | Seating Product |
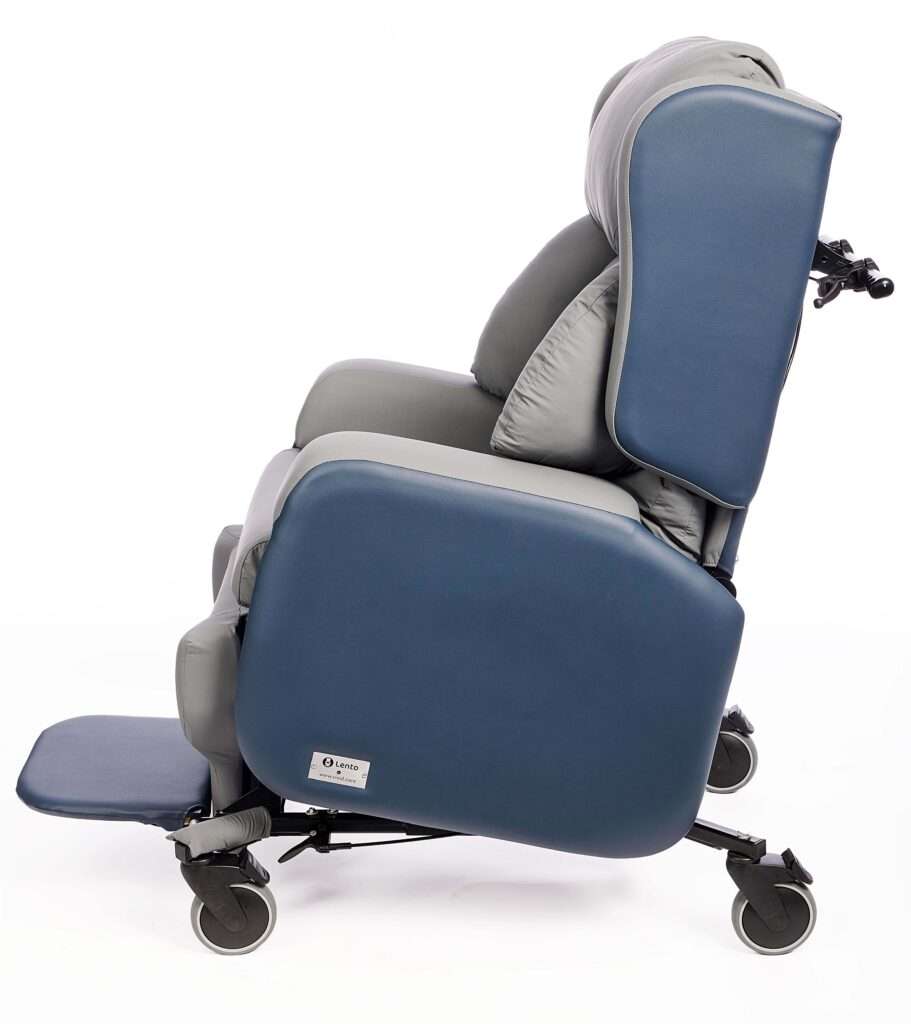
| Flexible backrest / adaptive posture chair | Provides back support but allows for pelvic movement and shifting — ideal when posture cannot be ‘fixed’ | Lento Care Chair – this chair allows seat width, depth, arm/leg/footrest adjustment, as well as tilt-in-space, backrest recline, adjustable/removable arms and a variety of backrest options.
|
| Adjustable head support | Offers head/neck support that moves with the user’s involuntary motions for cervical dystonia.
|
Multi Adjustable Headrest – with cushioned ‘fingers’ this cradles the user’s head and can be adjusted to any position.
|
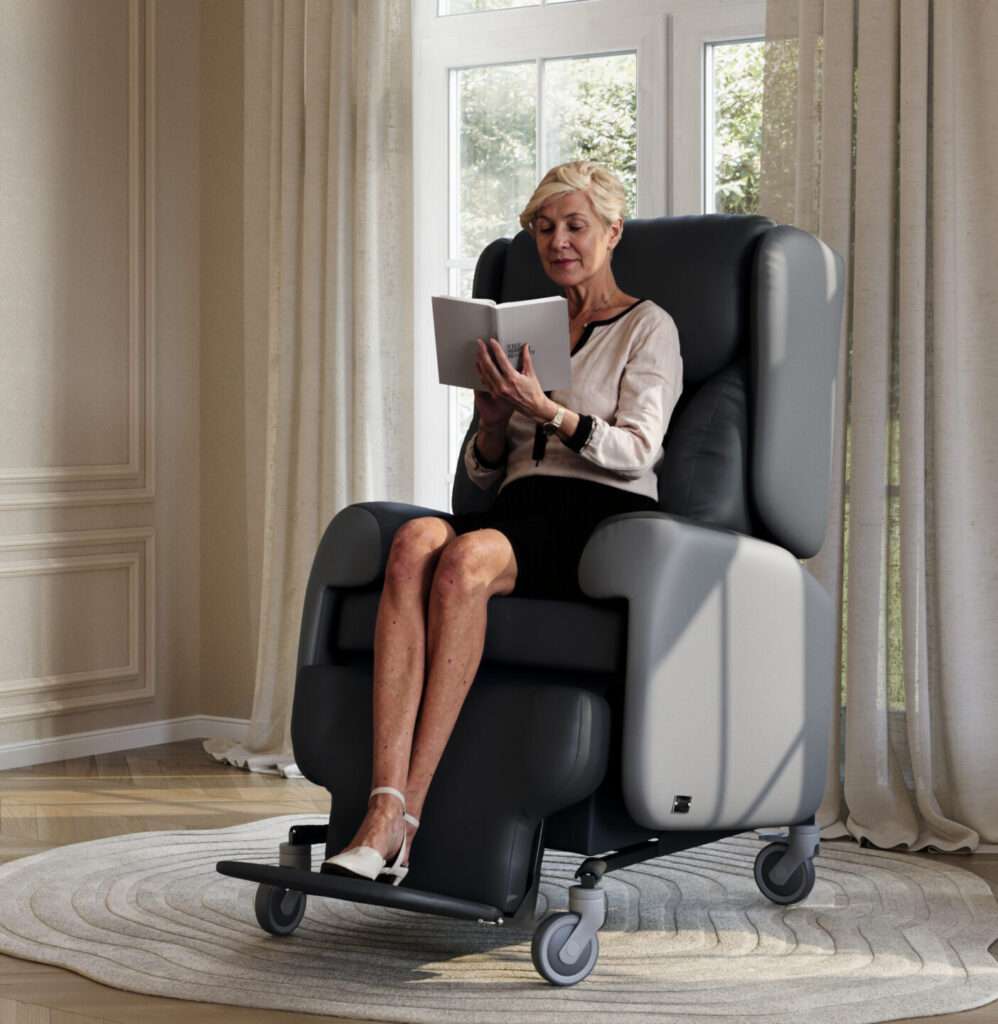
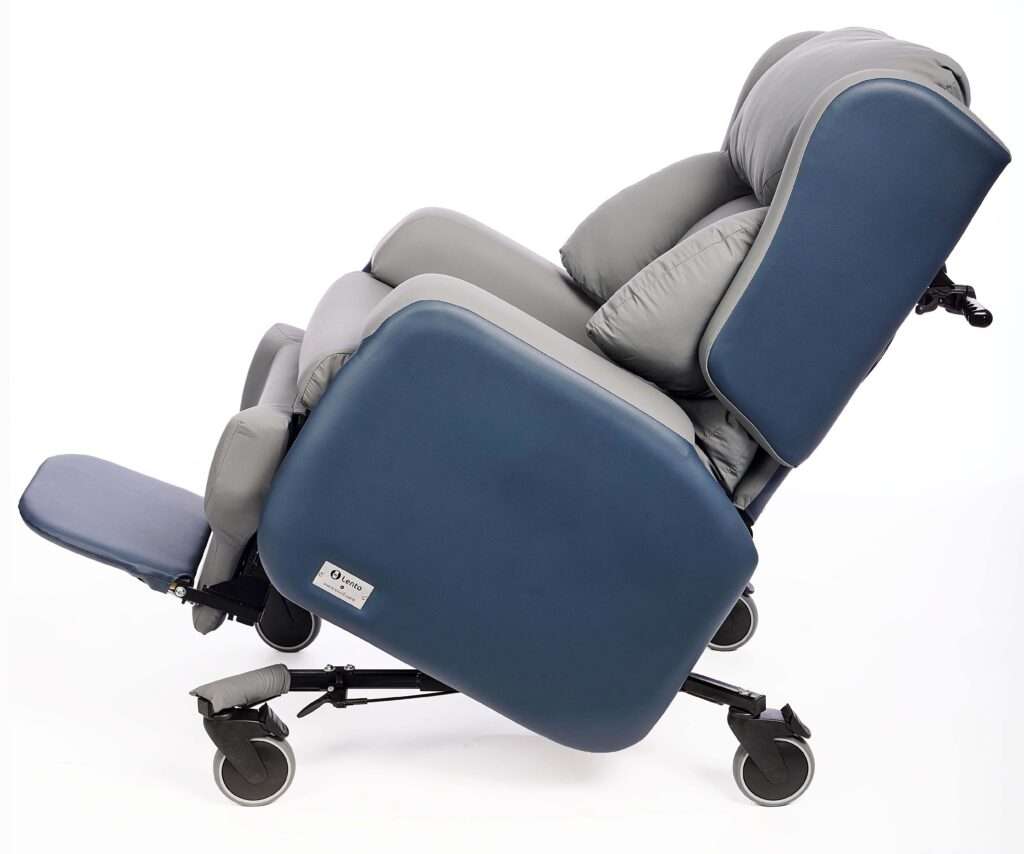
| Postural support chair with adjustable backrest and seat | Suited to complex neurological needs | Lento Cove Care Chair – offers a highly configurable 3-part backrest, individually adjustable cushioned arms, adjustable seat, tilt-in-space, and adjustable leg/rest/footplate – making it suited to people with complex posture or involuntary movements.
|
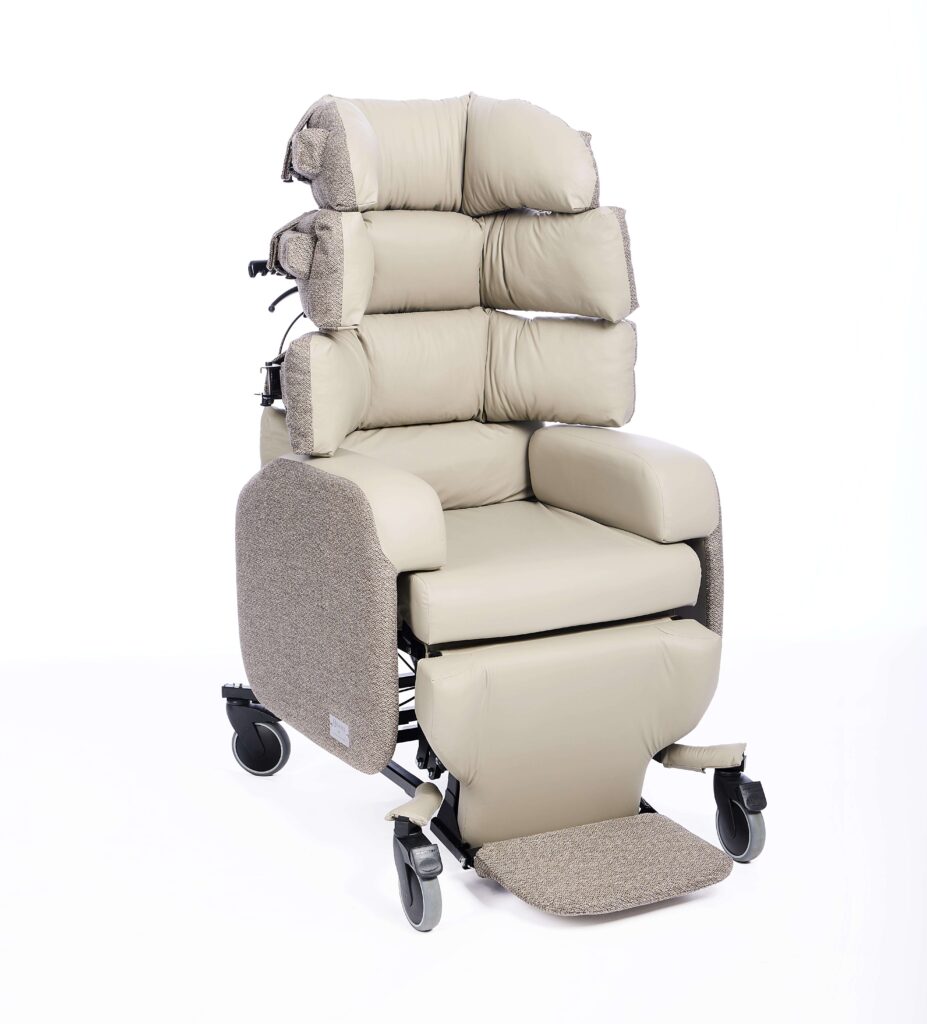

Lento Cove Care Chair
Final Thoughts
For individuals living with dystonia, and their families, caregivers, and therapists, seating is about achieving comfort, freedom, and functional participation.
A dynamic, flexible seating strategy accommodates the way the body wants to move and creates a more supportive, less stressful environment for daily life.
FAQs: Best Chairs for Dystonia
Q: Why is dynamic seating important for dystonia?
A: Because dystonia involves involuntary movement, seating must adapt with the body. Dynamic systems reduce resistance, discomfort, and the force of dystonic contractions.
Q: What key features should a dystonia-friendly chair have?
A: Flexible backrests, dynamic head supports, cushioned pelvic support, padded footplates, and adjustable seat width/depth are key seating features for dystonia. Tilt-in-space also helps with comfort and positioning.
Q: Why is pelvic support important?
A: A stable pelvis provides the foundation for upper-body movement and helps the user maintain comfort and efficiency during involuntary motions.
Q: What chair options work well for dystonia?
A: Highly adjustable, chairs such as the Lento Care Chair and Lento Cove Care Chair work well for dystonia.