The term ‘geriatric’ generally refers to people 65 or older. This is a growing demographic in the UK and currently stands at 12.7m people.
Winter can be a particularly challenging time of year for the geriatric population, with social isolation, icy weather and winter viruses combining to increase emergency hospital admissions for the elderly during the colder months.
Jump straight to…
Geriatric Hospital Wards
Geriatric wards in hospitals (or Medicine for the Elderly) provide acute care for vulnerable elderly patients. Geriatric patients tend to have comorbidities which make their health needs more complex, requiring simultaneous treatment of different conditions.
Examples of common conditions seen in geriatric wards are:
Arthritis
Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation and pain in the joints, affecting mobility. Depending on whether it is in the hands, legs or feet will affect a person’s ability to get in and out of a chair. Rise and recline chairs can be invaluable for arthritis sufferers.
Bowel problems
Constipation and incontinence are common problems in old age and can even be symptoms of conditions like bowel cancer or Parkinson’s. Constipation can be a function of not drinking and moving around enough, so it is important for regular routines to be observed.
Chronic pain
Chronic pain is often a function of underlying conditions like arthritis or back problems, but can be managed with the right therapy and medication. Our seating aims to maximise comfort, and bring therapeutic relief in the management of chronic pain.
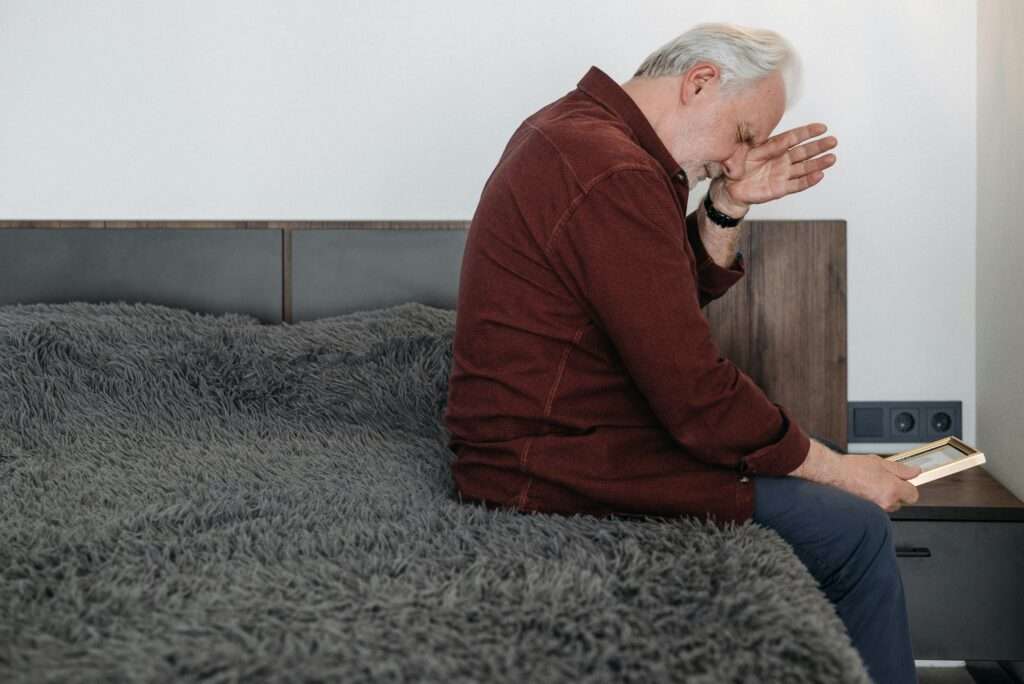

Delirium
A temporary cognitive disorder where the patient is confused and disorientated. More frail elderly patients are more susceptible to this, particularly post-surgery or when infections are present. As a temporary state, it tends to be indicative of an underlying problem, rather than a condition in itself.
Dementia
A progressive neurological disorder, characterised by a decline in cognitive functioning. It manifests itself in memory loss, general confusion and recognition problems, as well as changes in mood and personality. Physical side effects can occur in the more advanced stages of dementia, like incontinence and leaning to one side in a chair. Alzheimer’s is a common form of dementia.
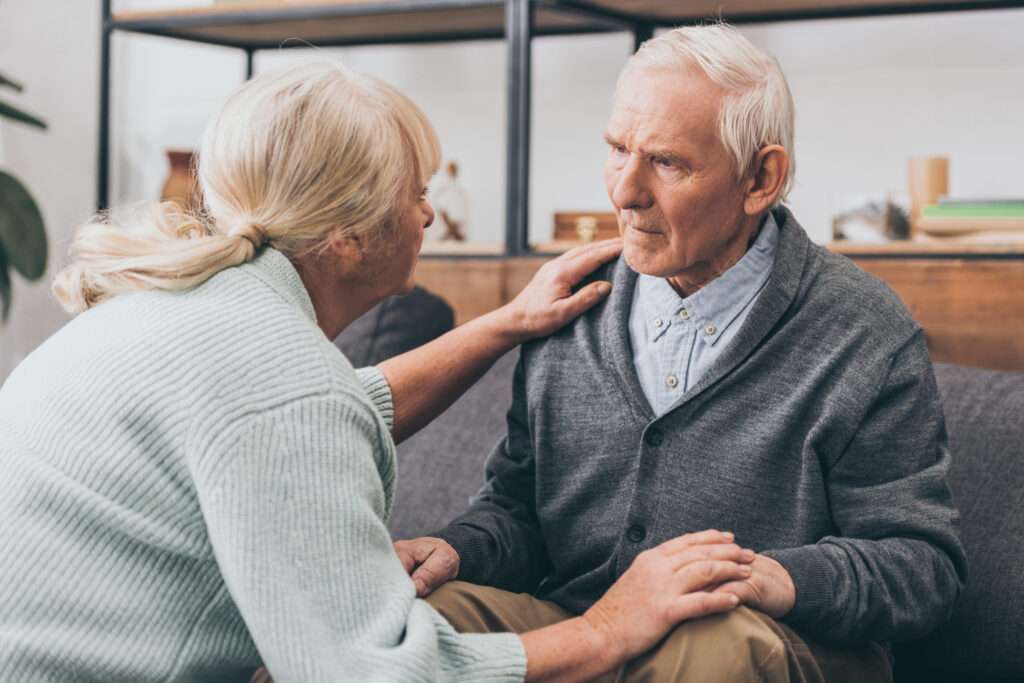

Falls and Syncope
Falls are a prevalent issue with the elderly due to a combination of factors such as poor mobility, balance and coordination problems, and syncope (fainting). Even falling out of a chair can be a common problem, with various seating design features that can help prevent this.
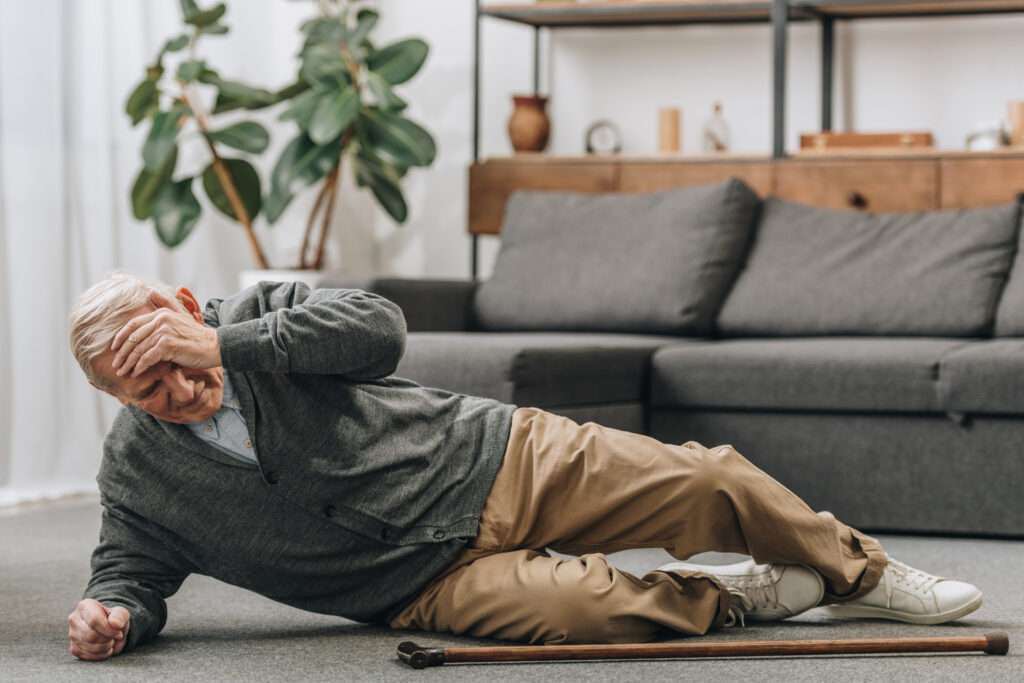

Leaning to one side
Leaning to one side in a chair is a common postural problem in seating, and one that can be caused by neurological causes such as dementia and strokes, as well as musculoskeletal issues.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that affects the bones, making them more fragile, due to reduction in the rate of new bone growth.
Need Specialist Seating?
Seating used in hospital geriatric wards needs to be designed with these different conditions in mind.
What is a Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA)?
Comprehensive Geriatric Assessments are used across healthcare disciplines to manage frail and vulnerable elderly patients.
As is often the case with healthcare assessments, they are multi-dimensional and take into account environmental and social factors to produce an integrated care plan for long-term use.

CGAs have improved patient outcomes and services across various healthcare settings.
- In acute hospital settings, CGAs have been shown to reduce falls and longer-term admissions. 1
- Utilising CGA in emergency departments such as Acute Frailty Teams and Same Day Emergency Care (SDEC) has lowered admission rates, functional impairment and re-admission to emergency care.2
- In surgical wards, integrating CGA into perioperative pathways has led to better recovery, lower cases of delirium and reduced admission to long-term care facilities.2
Try Our Chair Selector Tool
Best Seating for Geriatric Patients
Taking into account the various needs identified by the CGA (Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment) helps to inform the type of seating that geriatric patients need.
Comfort is a top priority for elderly people who spend large amounts of time in a chair, which is why we design all of our chairs with ergonomics, cushioning, and pressure care in mind. A comfortable armchair should not only provide exceptional support, but reduce pressure and promote good posture.
It’s also important to have adjustability to cater to a wide range of movement in the chair, which is why our chairs are highly adjustable and compatible with most transfer aids, for maximum independence and mobility.
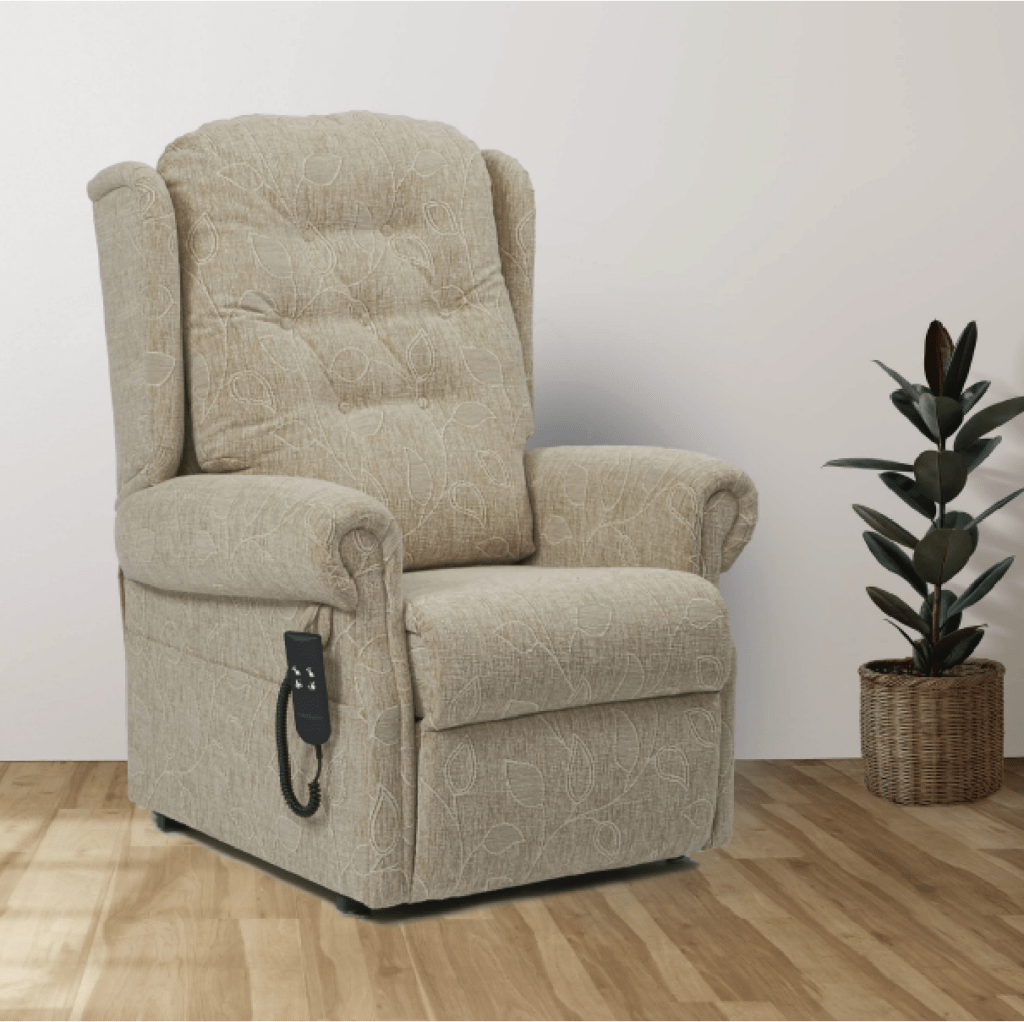
HiBack Bedside Chair
Our HiBack Bedside Chair was launched as a comprehensive solution to the age-old problem of hard and uncomfortable ward chairs.
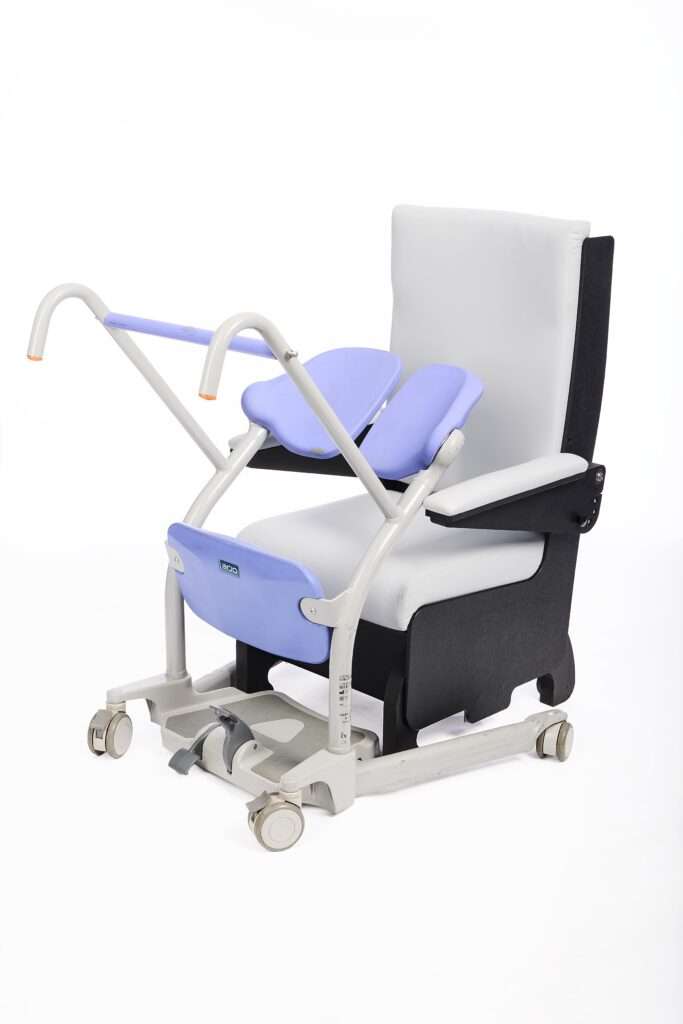
The traditional high seat chair used throughout hospital wards was proving to be inadequate in many areas, mainly:
- Hard and rigid design causing discomfort
- Difficult to adjust and move around the ward
- Poor hygiene and infection control
Our design addressed the needs of geriatric patients from first principles. The product development journey was an iterative process, involving lots of testing and trial-and-error to produce the finished product which incorporates the following features:
- Effortless height adjustment with an easy turn handle to adjust the chair to the right height for each person, helping prevent falls when transferring and making life easier for patients with dementia.
- Adjustable seat width and depth to ensure a perfect postural fit for each patient and prevent leaning to one side.
- Four-way stretch fabric and Levitex foam, relieving pain for those with higher pressure needs.
- Ergonomic design with slightly raked seat and angled backrest to reduce strain on the joints, helpful for arthritis and osteoporosis.
- Recess-free surfaces and removeable upholstery caters to the highest infection control standards, important for dealing with incontinence issues.
- Flexible armrests to assist with transfers and prevent leaning.
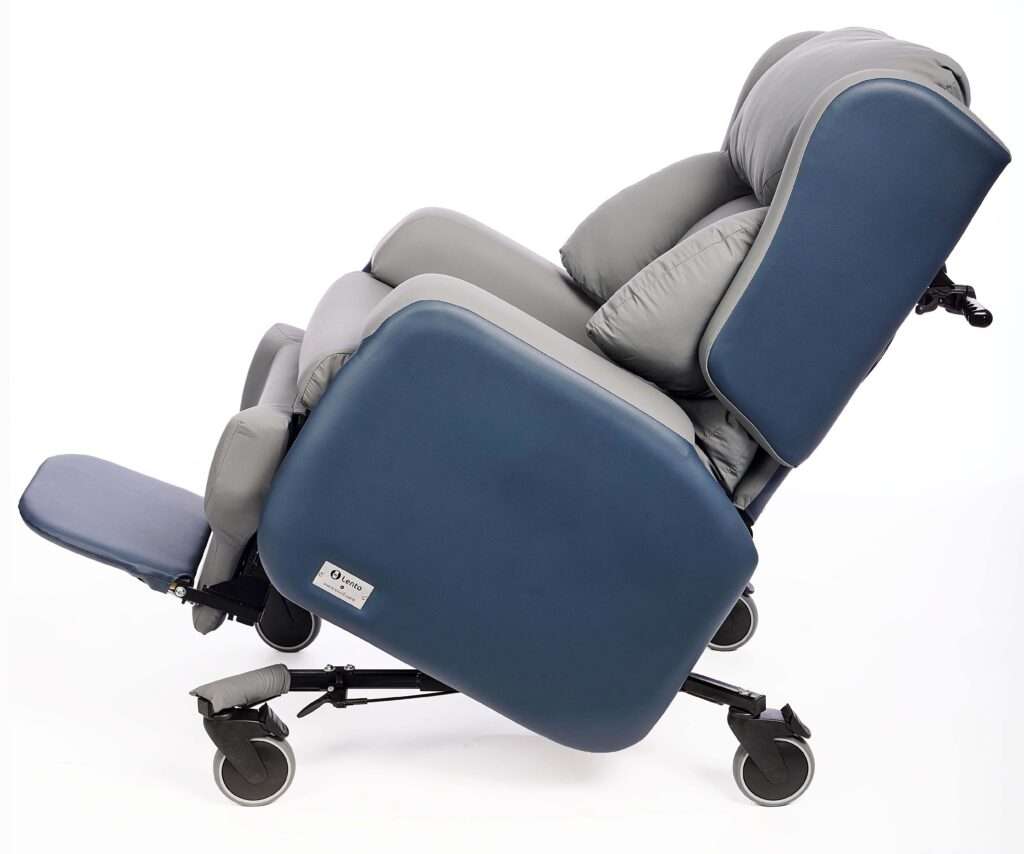
Lento Mobile Riser Recliner
Designed in collaboration with Manchester Royal Infirmary, the Lento Mobile offers all the comfort and functionality of a riser recliner while being slim and portable for moving around the ward.
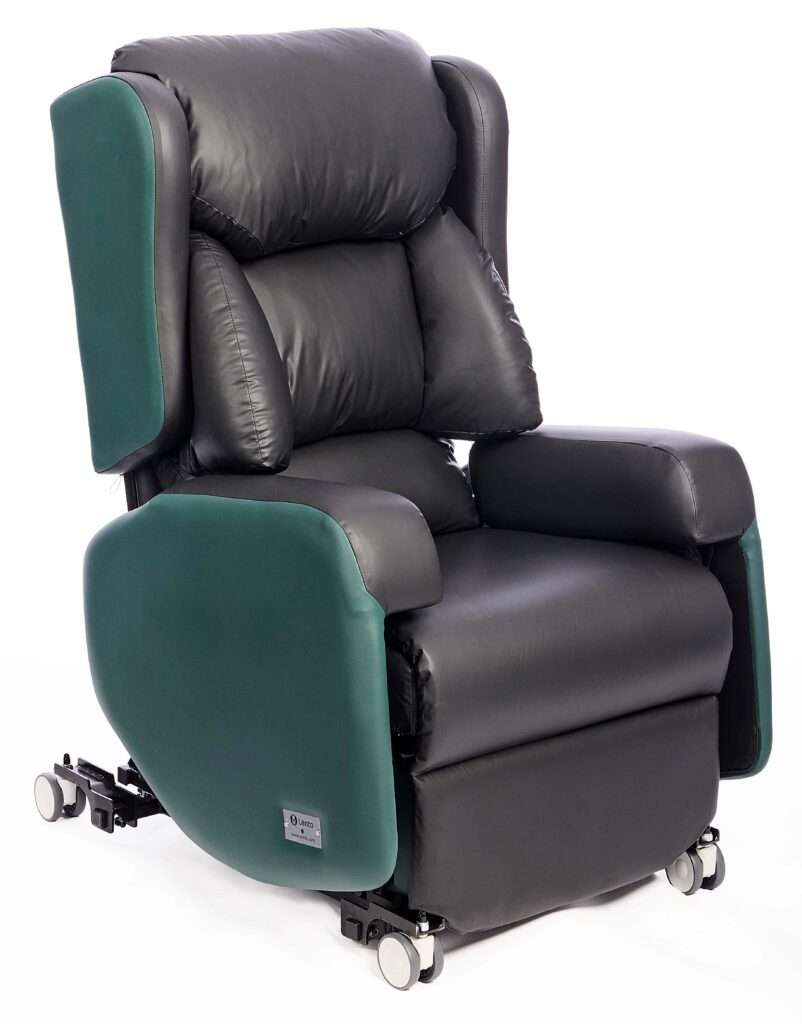

- The tilt-in-space function provides many health benefits, including better pressure relief and postural support.
- The independent backrest recline relieves pressure on the joints so is beneficial for arthritis sufferers, and the vertical rise helps those who may be unsteady getting to their feet.
- The interchangeable backrests have a variety of waterfall, lateral or cocoon cushions, providing extra support for those who tend to lean to one side.
- The sides of the chair remove to make cleaning quicker and easier, and all materials can withstand rigorous and regular cleaning.
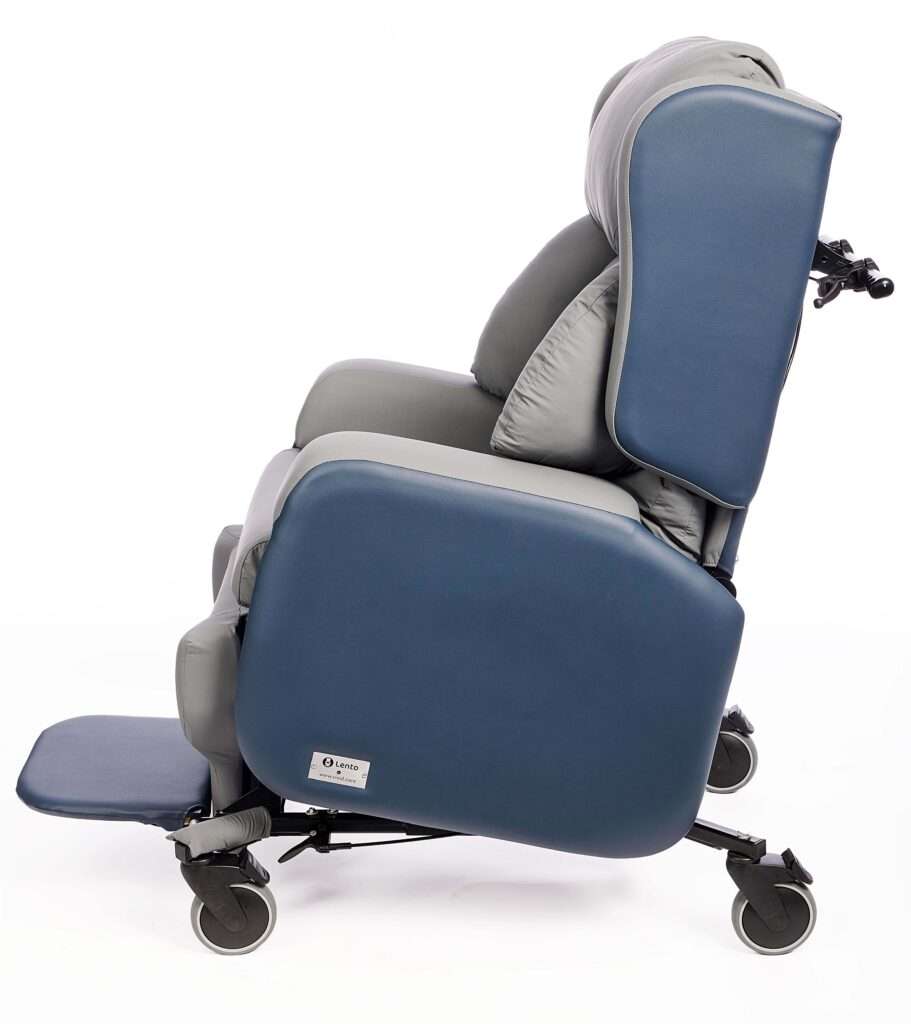
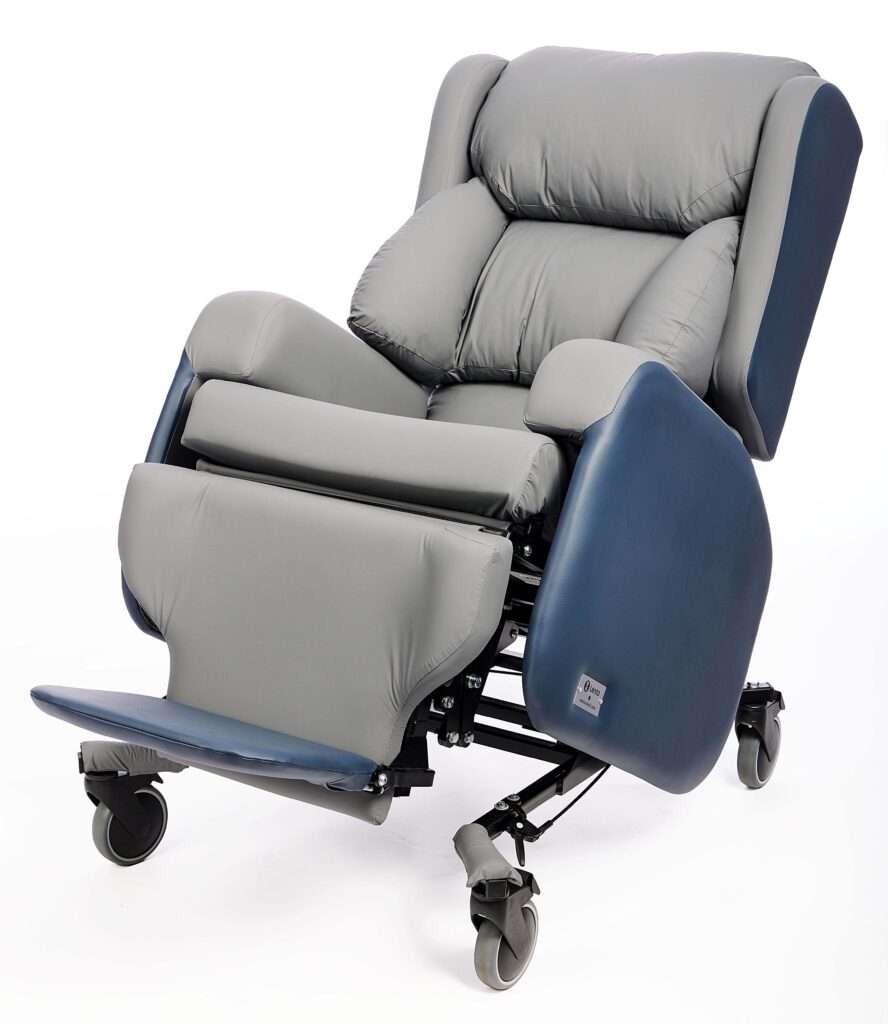
Lento Care Chair
Where a higher degree of postural support is required, the Lento Care chair can be used for those with more complex needs.
Suitable for anyone over 5’ 2”, the Lento Care chair is highly adjustable for any shape or size, and good for those who need hoisting.

Need Specialist Seating Advice?
Conclusion
Geriatric wards care for some of the most complex and vulnerable patients in the healthcare system. Understanding the wide range of physical, cognitive and medical conditions that older adults experience is essential for designing effective care environments, which seating plays a critical role in.
Investing in specialist seating for geriatric hospital wards helps clinicians deliver safer, more effective care while improving patient experience and treatment outcomes.
FAQs
What does geriatric mean?
The term geriatric refers to the branch of medicine focused on the health and care of older adults. It addresses age-related conditions, frailty, mobility issues, cognitive decline and multiple long-term conditions.
What age is geriatric?
In most healthcare settings, people aged 65 and over are considered geriatric. However, biological age, frailty and overall health are often more important than chronological age when assessing care needs.
What is a geriatric ward?
A geriatric ward (also known as Medicine for the Elderly) is a hospital ward specialising in the treatment of older patients with complex needs, comorbidities and reduced functional ability.
Why is specialist seating important in geriatric wards?
Elderly patients often spend long periods sitting and may have conditions such as arthritis, dementia, osteoporosis or chronic pain. Specialist seating improves posture, reduces pressure, supports safe transfers, helps prevent falls and enhances overall comfort and dignity.
What is a Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA)?
A Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment is a multidimensional evaluation that looks at a patient’s medical, functional, psychological and social needs. It is used to create a coordinated care plan and has been shown to improve outcomes across acute, emergency and surgical settings.
How does seating support CGA outcomes?
Appropriate seating supports mobility, independence, pressure care and posture, key factors identified in CGAs. Adjustable, ergonomic chairs help patients participate more actively in rehabilitation and daily activities.
References














