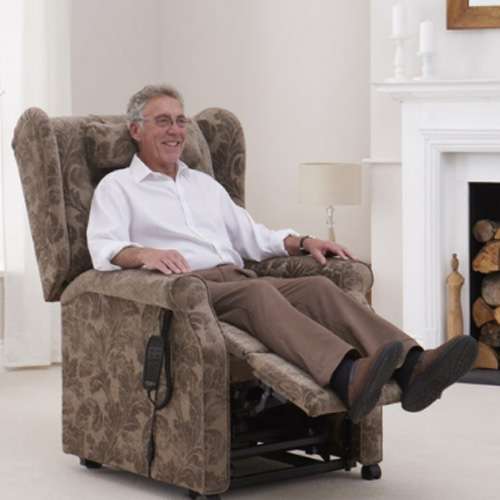
Within healthcare, providing providing patients with comfortable and supportive seating is crucial for their well-being.
Traditional seating designs can often fail to address the unique pressure points and ergonomic needs of individuals, which can lead to discomfort, poor posture, and even the development of pressure ulcers.
However, with the advancements in pressure mapping technology, healthcare professionals now have a powerful tool at their disposal to revolutionise seating design.
Key Takeaways:
- Traditional seating designs in healthcare often fail to address the unique pressure points and ergonomic needs of patients, leading to discomfort and potential pressure wound development
- Pressure mapping technology has revolutionised healthcare seating design by allowing designers to measure and analyse the pressure distribution between a person’s body and a seating surface
- Pressure mapping in healthcare seating helps identify areas of high pressure that can cause discomfort, skin breakdown and pressure ulcers, leading to improved patient comfort and well-being.
What is Pressure Mapping?
Pressure mapping in healthcare seating is a technique used to measure and analyse the pressure distribution between a person’s body and a seating surface.
This technology has become increasingly important in ensuring optimal seating solutions for patients, particularly those who are immobile or have limited mobility.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of pressure mapping in healthcare seating design and its impact in enhancing patient care.
Pressure Mapping Technology
Pressure mapping technology uses specialised sensors to measure and analyse the pressure distribution between an individual and a seating surface.
By capturing and visualising data on pressure points, healthcare professionals gain valuable insights into areas of high pressure that can cause discomfort or potential harm to patients.
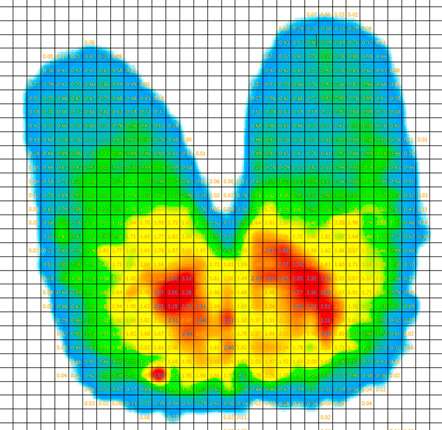
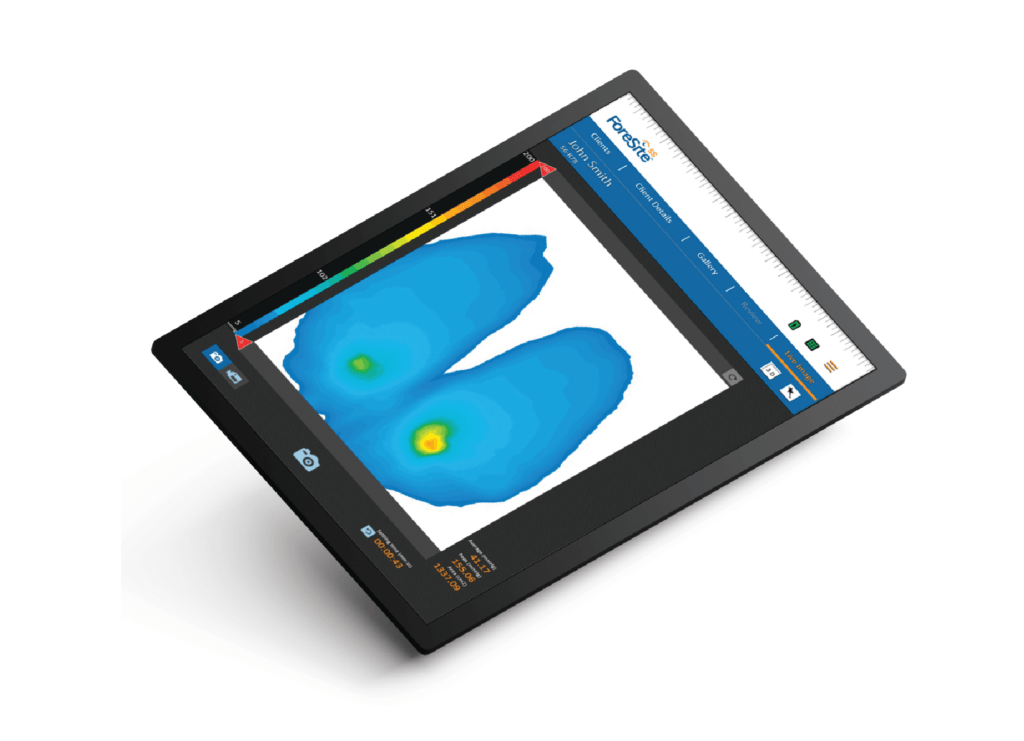
A pressure mapping image result of a person sitting in a chair (source)
These insights enable designers to create seating solutions that alleviate pressure and provide enhanced support, leading to improved patient comfort and well-being.
Pressure Mapping & Medical Seating
A pressure mapping assessment helps detect high-pressure points which cause discomfort and injury, promoting proper pressure redistribution and reducing the risk of sores.
Pressure mapping in healthcare seating allows healthcare providers to identify areas of high pressure, which can lead to discomfort, skin breakdown, and even pressure ulcers.
By using this technology, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about seating options and adjustments, ultimately improving patient comfort and overall well-being.
Pressure mapping for seating can provide details not accessible via visual inspection or subjective feedback alone. It reveals areas where excessive force is applied, allowing for precise adjustments based on a person’s body shape and weight distribution.
Interestingly, the use of pressure mapping technology has been widely accepted in many healthcare settings.

Pressure-sensitive sensors in cushions and seats identify areas needing more support. Innovative technologies such as 3D imaging technology allow patients to enjoy optimal seating without impacting their health and further boosts patient outcome quality.
How Pressure Mapping in Healthcare Seating Works:
In the section above, we learned that pressure mapping uses technology to measure the pressure between two interacting surfaces and displays this data as a computer image.
When measuring pressure in healthcare seating, designers look to use pressure mapping systems that allow them to test and compare against different body types.
Practically, this means placing a highly sensitive pressure mapping system between the patient and the surface they are ‘interacting’ with, in this case the seat.
The dynamic pressure sensors measure the points that are bearing the most/little pressure as a patient sits in their chair and represent this information as an on-screen image.
This information is crucial for the research and design of healthcare seating but also for healthcare staff who can use pressure mapping systems to determine what pressure systems can be recommend,
Healthcare professionals then make informed decisions about suitable devices to provide seating pressures.
Thus, reducing costs by avoiding unnecessary device purchases or replacements through a trial-and-error approach.
Further Considerations
Staff must be trained properly for efficient analysis of results. This way, additional tasks like prioritising seated patient assessments become manageable.
Routine evaluations with this tech should also be conducted to monitor progress over time & bring timely measures for better results.
Plus, applications in areas like wheelchair seating & healthcare settings. Benefits too, like reducing pressure ulcer risk & improving postural support.
Pressure Redistribution Features in Medical Seating:
Medical seating with pressure redistribution mechanisms is vital for patient comfort and safety in healthcare settings. These features involve various strategies, materials, and designs to reduce pressure points on the body.
Examples include:
- Pressure redistribution cushions
- Pressure-sensitive sensors
- Pressure relief technology
- Seating pressure management
- Pressure mapping systems
The objective is to distribute weight evenly across the user’s body area. Organisations can use pressure distribution analysis tools like pressure mapping technology or assess different designs and materials for medical chairs and beds.
This allows them to create solutions that meet individual needs.
Benefits of pressure redistribution include a decreased risk of sores/ulcers from immobility and improved comfort levels.
Factors to consider when customising are user dimensions, duration/severity of sitting, desired level of support, injury types/patterns, and more.
Through research, healthcare facilities can take advantage of new materials/technologies and improve medical care for those who need prolonged services with mobile/wheelchair-based utilities.